- Steps to Implement an Effective Employer Branding Strategy
- Leveraging Digital Channels for Employer Branding
- Employee Advocacy and Its Role in Employer Branding
- Measuring and Iterating Employer Branding Efforts
- Cross-Department Collaboration for a Strong Employer Brand
- Investing in Social Responsibility to Strengthen Employer Branding
- Career Development Opportunities as a Key Employer Branding Strategy
- Leveraging Data Analytics to Optimize Employer Branding Strategies
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Organizations use the strategic employer branding approach to present themselves as attractive workplaces for existing staff members and job candidates. The strategy works past recruitment because it shapes how employees engage with their work and their intent to stay and develops the workplace culture. The main distinction between corporate branding and employer branding stems from the consumer orientation in corporate branding versus the focus on the internal workplace environment and development opportunities in employer branding.
A company’s Employee Value Proposition (EVP) represents the distinct benefits and opportunities professionals receive upon exchanging their expertise with the organization. A compelling EVP functions as a powerful recruiting tool that simultaneously builds employee loyalty by linking organizational values with employee expectations. Glassdoor (2024) states that 75% of potential candidates check employer branding before applying. According to LinkedIn (2016), employer reputation quality results in a 50% reduction in hiring costs and better employee retention rates.
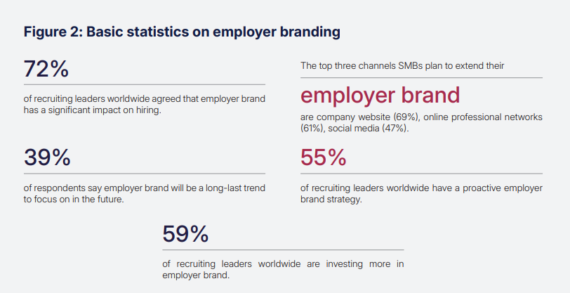
Statistics on employer branding
Most organizations build their employer brands using their social media reach, worker advocacy, and workplace guidelines and standards. An organization must verify the core beliefs in their workplace and external organizational perceptions to build an impactful employer brand and genuine employer brand. Employer Branding in the U.S. Market
The U.S. employment sector has become competitive as organizations strive to recruit excellent candidates. Recruiting leaders worldwide identify employer branding as a major factor in recruitment success; 72% of them state this is true (LinkedIn, 2016). Because of its essential nature, all organizations should make employer branding their main business priority.
A carefully planned employer brand gives businesses multiple advantages, including better recruitment success, used employee departure rates, and increased worker commitment. Businesses with highly regarded employer brands achieve 28% lower employee departure rates, thus lowering future expenses (Gallup, 2024). Social media reputation evaluation is a vital step in a job seeker’s application process, according to CareerArc’s 2021 findings, which reveal that 82% of candidates practice this behavior.
In the U.S. business market, employer branding creates positive work environments with transparent internal communication elements. The workplace brands of companies like Google and Microsoft succeed at attracting top talent because they provide flexible work scheduling combined with innovative approaches and meaningful work situations. Organizations that do not dedicate funds to building their brand will have their skilled staff migrate to companies whose reputations surpass their own.
Steps to Implement an Effective Employer Branding Strategy
A methodical implementation of employer branding demands that organizations evaluate their existing workplace reputation. Employee surveys, exit interviews, and reviews on Glassdoor and Indeed (Indeed, 2024) platforms enable such achievement.
The first step for organizations to develop their strategy is identifying their current Employee Value Proposition (EVP) through effective perception assessment. The employer branding strategy must present essential advantages that include professional development opportunities, organizational traditions, organizational traditions, payment benefits, and time management capabilities. Organizations that develop a precise EVP experience employee retention rates that drop by 69% (Gartner, 2024).
According to Vorecol (2024a), a positive recruitment experience shapes candidate decisions regarding job acceptances, with 78% of candidates confirming this. The combination of AI tools and chatbots enhances organization communication while ensuring quick responses, streamlining the complete recruitment process.
Organizations should track their employer branding strategy through essential performance indicators (KPIs), including retention rates, time-to-hire, and the Net Promoter Score (NPS) to keep their employer brand strong. Organizations that implement routine feedback systems gain the ability to adjust their workforce expectations through changes in market needs.
Leveraging Digital Channels for Employer Branding
Employer branding underwent a radical transformation through the internet because it provides enhanced visibility of corporate reputations. Today, social media platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Instagram serve as critical touchpoints for employer branding. The data shows that job seekers rely on social media to assess company culture as a mandatory step before considering employment (CareerArc, 2021).
A well-established online footprint helps job seekers receive continuous messages about organizational values and the work environment. When companies participate in Glassdoor activities, job application numbers rise by 75% (Glassdoor, 2024). According to McGowan (2019), Patagonia achieves success through social media by showing its dedication to environmental sustainability, thus attracting employees who share similar values.
Employers can improve their content through analytics tracking, which measures employee impact on their digital presence. Businesses can optimize their branding strategy by combining tools, including Google Analytics, LinkedIn Insights, and Tableau, which provide valuable data about candidate behavior.
Employee Advocacy and Its Role in Employer Branding
Employee advocacy provides the best and least expensive support for a company’s employer brand. Letting employees post about their favorable workplace experiences through LinkedIn and Glassdoor will tremendously boost a company’s public image. Studies demonstrate that employee material generates eight times more engagement than corporate official posts (Neal, 2024).
IBM’s employee advocacy program provided incentives to workers, leading to a 30% boost in job referrals, according to IBM (2024). Organizations must teach their workforce about advocacy programs and establish rewards to motivate them to participate.
Both junior and senior staff members possess the capacity to affect employer branding initiatives. According to Gray (2022), the impact of content posted by workers at the organization level remains equivalent to messages transmitted by executive leaders. To promote employee branding through ambassadorship, organizations must support open transparency and active communication between staff members.
Measuring and Iterating Employer Branding Efforts
Employer branding continues as a continuous cycle that demands regular assessments that lead to improvements. Businesses need to track particular KPIs as indicators of their branding success. Employer branding assessments rely on three key metrics, including time-to-hire, retention rates, and cost for each hired candidate.
Through data-based strategic enhancement, organizations achieve better recruitment results and lower hiring expenses. IBM’s implementation of analytics generated 35% more suitable applicants while cutting hiring expenses by 20% (Vorecol, 2024c).
Implementing ongoing feedback systems that businesses need to deploy should improve workplace culture. Walmart’s open-door policy enables staff members to express their concerns, which results in better workplace engagement for employees (Liude, 2024).
An organization’s ability to monitor its branding strategies continuously and adapt to changing workforce requirements enables it to stay competitive and deliver.
Cross-Department Collaboration for a Strong Employer Brand
The responsibility for employer branding exceeds the scope of the Human Resources (HR) department. Effective branding efforts require teams from the Marketing, leadership, and Communications departments to work together to maintain consistent messaging and brand identity. Research shows that organizations deliver enhanced employee engagement and better brand quality by connecting employer branding to their corporate strategic model (Graham & Cascio, 2018).
The HR department, through its responsibility for employee engagement and recruitment strategies and performance management functions, helps create a strategic alignment between employer branding initiatives and internal company culture. Marketing teams create powerful messages, which they distribute through LinkedIn, Glassdoor, and company websites. Executive leaders touch on the most critical aspect of company success through value representation and developing a desirable cultural environment for employees.
The comprehensive model established by Salesforce demonstrates exceptional teamwork between departments as it weaves employer branding within corporate service programs and inventive methods. The company uses philanthropic and sustainable initiatives to draw personnel who care about social responsibility. LinkedIn (2016) reveals that employer branding strategies are active in 55% of companies worldwide, thus demonstrating why teams from various departments need to collaborate (LinkedIn 2016).
When U.S. employers combine departments, they develop a single employer brand message that boosts employee engagement and strengthens external perceptions, creating a workforce that is more attractive to competitors.
Investing in Social Responsibility to Strengthen Employer Branding
CSR is essential in employer branding because job seekers depend on it when choosing their future employers. Modern employees make decisions about their employment based on purpose-driven organizations that commit to sustainability, diversity, and ethical business standards. Most American job seekers seek employment at businesses that demonstrate robust social responsibility values (Stobierski, 2021).
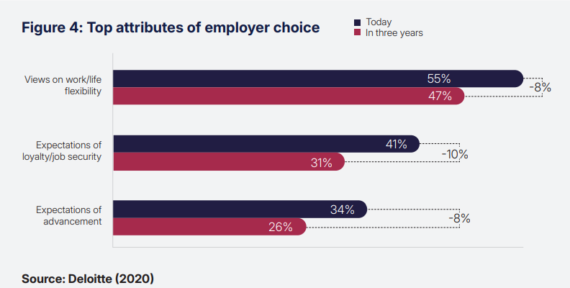
attributes of employer choice
The employer brand of Patagonia and similar companies benefits from their CSR activities. Through its “1% for the Planet” charitable program, Patagonia establishes itself as an industry leader for eco-minded candidates seeking employment (Patagonia, 2024). Microsoft has built sustainability programs into its corporate structure, which activate staff dedication and beckon highly qualified workers who value ecological and social progress (Boyd, 2024).
Companies that support social responsibility initiatives achieve three primary benefits through their investments: they gain higher employee involvement, a better public reputation, and a higher number of attracted skilled applicants who value social responsibility. A correlation between employer branding and corporate social responsibility initiatives enables businesses to stand out for skilled talent and maintain workforce members driven by social contribution.
Career Development Opportunities as a Key Employer Branding Strategy
Career development programs can help organizations build a strong employer brand. According to Deloitte (2020), 73% of workers consider this their employers’ top responsibility.
Extensive employee training programs implemented by Amazon and Google have established career development standards for other organizations. Amazon supports employee success through the Career Choice Program, which gives full tuition reimbursement for training, leading to high-demand careers (Bourque, 2022). Google provides employees with mentorship opportunities through the “Career Guru” mentorship program that promotes continuous learning (Vorecol, 2024b).
Organizations that dedicate resources to employee growth initiatives enhance their reputation while boosting employee performance and retaining talent. Employers in the U.S. need to establish career development initiatives because their workers prefer companies that provide continuous learning and career advancement opportunities.
Leveraging Data Analytics to Optimize Employer Branding Strategies
Organizations should use data-driven methods to direct their employer branding initiatives in the digital era because data enables adaptability and success. Organizations that make branding decisions based on data analytics succeed in cutting recruitment expenses and achieving hiring performance improvements (Gartner, 2024).
The assessment of employer branding success relies heavily on key performance indicators (KPIs), which include time-to-hire, retention rates, candidate conversion rates, and Net Promoter Score (NPS). Implementing recruitment analytics at IBM enhanced qualified candidate attraction by 35% and decreased hiring costs by 20% (Vorecol, 2024c).
Organizations benefit from three AI-driven tools: LinkedIn Insights, Glassdoor Analytics, and Beamery recruitment software. These tools provide important information about candidate actions and employee emotions, along with talent acquisition statistics. This enables organizations to improve their job descriptions, EVP communication methods, and employee engagement initiatives.
U.S. employers should use data analytics to develop exact employer branding approaches that will help them stay competitive in the shifting labor market. Monitoring employer brand performance and its evaluation enables organizations to understand workforce demands better for ongoing improvement of talent attraction methods.
Related Articles
A successful social media marketing strategy for B2B success depends on trust development while sharing valuable content that targets decision-making [...]
Every employer understands the importance of retaining their employees because this is one way through which their business can grow [...]
Email marketing represents an effective strategic tool for business growth in the online field. Your email marketing strategy requires active [...]
The competitive marketplace demands that businesses go beyond the ordinary and stand out as the key to success. Trust is [...]





